What is a Citizen Developer? (Complete Guide & Tools)

Niamh Conneely | Marketing Executive
The rise of the ‘citizen developer’ is increasing rapidly. This guide shows you what it means to be a citizen developer, exploring how this role is reshaping the creation and implementation of digital solutions.
From defining the concept to examining its impact and potential, we’ll take a look at the essentials of becoming a citizen developer, the tools available, and the future of this growing field.
What is a citizen developer?
Citizen developers are changing the game in business technology. They’re not your typical IT professionals; instead, they’re everyday employees who step up to create or modify business applications by themselves. This shift is significant when understanding the citizen developer definition, it’s about empowering regular employees to take charge of software development without waiting for IT department approval. In the past, even minor changes or new projects could get stuck in long IT queues, slowing down progress and allowing competitors to take advantage.
These citizen developers bring speed and flexibility to the table. They can quickly respond to changing business needs, speeding up the creation and updating of applications. This not only speeds up innovation but also lightens the load on IT departments, freeing them to tackle bigger, company-wide issues. Plus, by working openly and sharing resources with IT professionals, citizen developers help keep everything secure and in line with the company’s tech strategy.
In short, citizen developers make businesses more agile and efficient by taking software development into their own hands.
How to become a citizen developer?
Becoming a citizen developer opens up new avenues for innovation and problem-solving within a business. Here’s how you can start your journey:
- Learn the basics: Start with understanding the fundamentals of software development. You don’t need to become an expert coder, but having a basic grasp of how applications work, what programming is, and how databases function can be incredibly helpful.
- Get familiar with low-code/no-code platforms: One of the hallmarks of citizen development is the use of low-code or no-code platforms. These tools are designed to be user-friendly and intuitive, allowing you to build applications with minimal coding. Spend time exploring platforms like Fliplet and practice building simple applications.
- Understand your business needs: As a citizen developer, your strength lies in your knowledge of your business’s needs and processes. Identify problems or inefficiencies within your organization that could be addressed with a custom application.
- Collaborate with IT: While citizen development empowers you to build applications independently, it’s still important to maintain a collaborative relationship with your IT department. They can offer guidance on data security, compliance, and integration with existing systems.
- Learn from online resources and communities: There are numerous online courses, forums, and communities dedicated to citizen development. Platforms like Udemy, Coursera, or even specific community forums on low-code platforms can offer valuable insights and learning resources.
- Start small and scale up: Begin with small projects that can be managed easily and have a clear impact. As you gain confidence and experience, you can take on more complex projects.
- Stay updated: The field of technology is always evolving. Stay informed about the latest trends and updates in low-code/no-code platforms and software development in general.
To help get you started take a look at our recent blog, How to Build a Custom App Without Any Coding (6 Steps)
By following these steps, you can transition into the role of a citizen developer, contributing to your organization’s technological innovation and efficiency from a unique, user-centered perspective.
Gartner stats about citizen development

Gartner’s research provides insightful statistics and perspectives on the rise of the citizen developer.
Definition and growth
Gartner defines a citizen developer as an employee who creates applications for themselves or others using tools approved by IT or business units. They typically use low-code and no-code platforms for building internal applications, integrations, workflows, and processes.
Driving factors
Despite the increasing number of software engineers and their high productivity, there is a growing demand for non-technical employees to develop their own software solutions. This demand arises from the constant expansion of software developer workloads, leading to project backlogs and a need for immediate, on-demand software solutions.
Advantages of citizen development
- Speed and accessibility: Non-technical makers can quickly ship websites and apps using no-code platforms. These platforms provide pre-built functionalities, allowing for the creation of software without programming experience
- Cost-effectiveness: Traditional development can be costly, ranging from $40,000 to $250,000. In contrast, citizen development using low-code and no-code platforms can produce full-featured applications at a fraction of the cost and time
- Agility: Citizen developers can adapt and change applications more swiftly than traditional software teams, enhancing the agility of the software development process
Industry impact and future trends
- 72% of IT leaders report that project backlogs hinder them from focusing on strategic projects. Citizen development is seen as a solution to this, shifting software demand to a collaborative effort across organizations
- There’s a notable difficulty in hiring qualified engineers, with 82% of organizations facing this challenge. Citizen development is growing to fill this gap, evidenced by 84% of enterprises adopting low-code and no-code tools
- The market demand for citizen developer apps is projected to grow at least five times faster than what traditional IT departments can support, leading to an estimate that 75% of the large enterprise will be using at least four no-code low-code development tools for IT and citizen development initiatives by 2024
- 61% of companies either have or planned to have functional citizen development initiatives
In conclusion, Gartner’s statistics and insights paint a picture of a rapidly evolving landscape where citizen developers are becoming increasingly central to organizational agility, innovation, and efficiency in the software development process.
The need for citizen development
Citizen development is rapidly becoming a vital part of modern business practices, mainly due to its significant impact on efficiency and productivity. Businesses that have embraced this community have noticed a marked improvement in their operations.
Traditionally, companies often found themselves waiting for IT departments to address various issues, leading to delays and inefficiencies. However, with the adoption of citizen development, many companies are now actively engaging in application creation themselves, bypassing these delays and accelerating their response to business needs.
The role of employees in this transformation is crucial. Those who learn and master low-code/no-code platforms become valuable assets, effectively functioning as in-house software developers. They are not only able to address their software needs but can also share this knowledge with colleagues, further expanding the citizen developer community within the organization.
This communal learning and application of low-code/no-code platforms leads to a ripple effect, enhancing operational efficiency across various business processes. As more employees become proficient in these platforms, the entire organization becomes more agile, responsive, and efficient.
Discover Why Organizations should embrace Citizen Developers.
Pros and cons of citizen development
Pros of citizen development
- Reduces burden on IT departments: Citizen development alleviates the workload on IT by enabling non-IT employees to create apps using low-code/no-code platforms. This allows IT staff to focus on other critical tasks and better manage the risks and requirements of app development
- Cost-effective: It creates a larger pool of employees capable of developing software, reducing reliance on IT professionals. This sharing of resources and tools within the citizen developer community is both economical and educational
- Increases productivity and efficiency: Low-code/no-code platforms accelerate app development and allow for quicker adaptations, enhancing overall efficiency and productivity within the organization
Cons of citizen development
- Constantly changing technology: Citizen developers need ongoing training to keep up with frequent updates in technology. Newcomers to this field often require additional guidance to become proficient
- Questionable quality: Without adequate oversight from IT professionals, the quality of applications developed by citizen developers can be inconsistent. IT’s involvement remains crucial in ensuring the functionality, security, and overall quality of the final product
Citizen developer vs professional developer comparison
The rise of citizen development can be traced back to the realization that professional developers were overburdened, juggling both the creation and maintenance of applications. This often led to a backlog, with projects stagnating in queues for months.
Enter the citizen developer, empowered by low-code/no-code platforms, capable of building applications despite lacking professional development experience. These individuals often possess deep knowledge in their specific domains, enabling them to craft applications that closely align with the needs of their users.
Today, businesses are recognizing the importance of balancing the agility and user-centric focus of citizen developers with the security and oversight provided by professional developers. As citizen development continues to grow, this balance becomes crucial in harnessing the strengths of both worlds for effective application development.
What types of citizen developers exist?
Citizen developers can be categorized based on their roles and the types of applications they create. Here are a few common types:
- Business analysts: They often use citizen development tools to automate and optimize business processes, create data models, and develop reporting tools
- Project managers: Utilizing citizen development to streamline project management processes, they might develop customized dashboards or tools for better project tracking and communication
- Marketing professionals: In marketing, citizen developers might create tools for campaign management, customer engagement analytics, or social media integration
- HR professionals: They could develop applications for employee onboarding, training programs, or internal communication platforms
- Customer service representatives: These citizen developers might build chatbots, customer feedback tools, or support ticketing systems
- Event managers: These citizen developers create tools to streamline their event, and make their events more engaging for the attendees.
Each type of citizen developer brings their domain expertise to the development process, creating applications that are closely aligned with the specific needs of their field.
Characteristics of a Star Citizen Developer
A citizen developer stands out by displaying these standard characteristics such as:

- Problem-solving skills: They excel at identifying challenges and creating effective solutions
- Tech-savvy: Possess a strong grasp and interest in technology and digital tools
- Learning agility: They should be quick to adapt and learn new technologies and processes
- Collaborative mindset: Work effectively with teams and stakeholders, both technical and non-technical
- Creative: Find different ways to approach and solve problems
- Innovative: Continuously seek and apply new ideas to improve processes and products
- Adaptability: Flexibly adjust to new challenges and changes in the business environment
- Attention to detail: Ensure precision and accuracy in all aspects of development
- Good communicator: Articulate ideas clearly and effectively, facilitating better understanding and collaboration
RPA citizen developer
An RPA (Robotic Process Automation) citizen developer is an individual, typically a business professional, who uses RPA tools to automate manual and repetitive tasks within business processes. They aren’t traditional software developers; instead, they have learned to use RPA platforms to create bots that mimic human actions in digital systems. Here are some of the characteristics of a RPA citizen developer:
- Automating processes: Skilled in using Robotic Process Automation (RPA) tools to automate repetitive tasks
- Analytical thinking: Able to analyze business processes and identify opportunities for automation
- System integration understanding: Knowledgeable in integrating RPA solutions with existing systems and databases
Citizen developer for low-code platforms
- Platform proficiency: Expertise in using low-code platforms to build applications
- User-centric design: Focuses on creating user-friendly interfaces and experiences
- Rapid prototyping: Capable of quickly developing prototypes and iterating based on feedback
Data-driven citizen developer
- Proficiency in data tools: Skilled in using data analysis and visualization tools
- Insightful data interpretation: Able to translate data into actionable business insights
- Data integration skills: Expertise in integrating data sources for comprehensive analysis
Citizen developer for business analytics
- Business process understanding: Deep knowledge of business processes and needs
- Analytical mindset: Ability to analyze trends and performance metrics
- Reporting and dashboard creation: Skilled in creating insightful reports and dashboards
Mobile app citizen developer
- Mobile platform knowledge: Understanding of mobile platform capabilities and limitations
- User experience focus: Emphasis on intuitive and responsive mobile app design
- Cross-platform development: Ability to develop apps that work across various mobile operating systems
Discover the The Top 10 Best App Builders to Create a Mobile App
Programs to become a citizen developer
Embarking on a journey to become a citizen developer involves accessing the right resources and training programs. These programs are designed to equip aspiring citizen developers with the necessary skills in low-code/no-code platforms, understanding of software development principles, and practical application in a business context.
PMI citizen developer
Project Management Institute (PMI) offers comprehensive resources for citizen developers, focusing on project management and development skills. PMI Citizen Developer.
Microsoft Power platform training
Microsoft Power platform training offers courses on using Microsoft’s suite of low-code tools.
Salesforce trailhead
Salesforce trailhead provides training for building apps using Salesforce’s low-code solutions.
Appian Academy
Appian Academy offers training on Appian’s low-code automation platform.
Mendix Academy
Mendix Academy teaches people how to build applications using the Mendix low-code platform.
Do these programs include a citizen developer certification?
Many of these programs offer certifications upon completion, providing official recognition of the skills acquired and enhancing the credibility of the citizen developers. These certifications can be a valuable asset in professional development and career advancement.
What frameworks should a citizen developer use?
For citizen developers, selecting intuitive and powerful frameworks is crucial for effective application development. Let’s focus on a key framework that fits this description, Model-View-Controller (MVC).
The MVC framework is a way to organize and structure your application. It divides the application into three interconnected components:
- Model: This is where your data lives. Think of it as the heart of your application’s data management – it represents the data itself and the rules around how that data can be changed
- View: This is all about the user interface. The View component displays the data from the Model to the user in a specific format. It’s what your users see and interact with, like web pages and forms
- Controller: This part acts as an intermediary between the Model and the View. It processes all the input received from the user through the View, possibly altering the Model as a result
MVC is particularly helpful for citizen developers because it compartmentalizes different aspects of application development. You can modify the visual aspect of your application (the View) without needing to delve into the data management logic (the Model). This separation makes it easier to manage, update, and troubleshoot your application.
Advantages of this framework includes:
- Improved organization: By separating concerns, MVC makes it easier to manage complex applications, breaking down the development process into manageable parts
- Enhanced maintainability: Updates or changes in one component (like the user interface) can be made independently of others (like the data model), simplifying maintenance
- Reusable components: Elements in the MVC framework, especially in the View, can often be reused across different parts of the application, saving time and effort
- Easier collaboration: With distinct separation of concerns, different team members can work on different components simultaneously without causing conflicts
- Increased scalability: MVC architecture allows for scalable application development, making it easier to expand or upgrade the application over time
- Facilitates test-driven development: Each component can be tested independently, making it ideal for test-driven environments
By using the MVC framework, a citizen developer can efficiently organize the development process, making it more manageable and less overwhelming, especially when dealing with complex applications. This framework provides a structured yet flexible approach to building software, making it a popular choice among those new to application development.
Citizen development (tools & platforms)
In the world of citizen development, having the right tools and platforms at your disposal is key to success. These tools and platforms empower users with little to no traditional coding experience to create applications that can transform business processes and workflows. Let’s explore some of the top tools and platforms available for citizen developers.
Top citizen developer tools
1 Zapier

Zapier is a versatile tool for automating workflows. It seamlessly connects a multitude of apps and services, allowing for the creation of automated processes without the need for coding. Users can easily set up triggers and actions across different applications. For example, you can create a workflow where new email attachments are automatically saved to a cloud storage service, or where new social media posts trigger notifications in a team chat app. Zapier’s ease of use and extensive app integration make it a favorite among citizen developers.
2 Trello

Trello is an intuitive project management tool widely used for its simplicity and visual interface. It organizes projects into boards, lists, and cards, enabling teams to track progress and collaborate effectively. Each card can represent a task or an idea, which can be moved across lists to show progress. Trello is flexible, catering to various project management needs from simple to-do lists to complex workflow tracking. It integrates with other tools and services, enhancing its utility in managing projects and team collaboration.
3 Airtable

Airtable combines the ease of a spreadsheet with the robust functionality of a database. It’s a powerful tool for citizen developers who need to organize and manipulate data without the complexity of traditional database software. Users can create custom databases that look like spreadsheets but have the capability to handle complex tasks like linking related records, attaching files, and integrating with other apps. Airtable’s user-friendly interface and customizable features make it suitable for a wide range of applications, from content management to inventory tracking.
Top citizen developer platforms
1 Fliplet

Fliplet offers a no-code/low-code platform that greatly simplifies app development for non-technical users. Its drag-and-drop interface allows for the easy creation of apps for various business purposes. Users can build everything from internal communication tools to customer-facing applications without needing to write any code. Fliplet’s emphasis on accessibility and ease of use makes it a standout choice for citizen developers looking to create functional, professional-looking apps with minimal technical expertise.
2 UI Path for citizen developers

UI Path provides a robust platform for automating repetitive office tasks, making it highly valuable for citizen developers in corporate environments. It specializes in Robotic Process Automation (RPA), allowing users to create bots that automate routine tasks like data entry, file manipulation, and even complex workflows. UI Path’s user-friendly interface and powerful automation capabilities help non-technical staff to increase productivity and efficiency by reducing the time spent on mundane tasks.
3 Microsoft for citizen developers

Microsoft offers a suite of tools tailored for citizen developers, including Power BI, Power Apps, and Power Automate. Power BI is a business analytics tool that enables users to create interactive reports and dashboards. Power Apps allows for the creation of custom apps to solve business needs without extensive coding. Power Automate (formerly Microsoft Flow) is a tool for automating workflows across various applications and services. These tools provide a comprehensive ecosystem for citizen developers to build custom solutions and automate processes within the Microsoft environment.
4 ServiceNow for citizen developers

ServiceNow, traditionally known for its IT service management capabilities, also provides robust application development tools for citizen developers. It enables users to build and deploy custom applications that can automate workflows and streamline business processes. The platform’s low-code development environment allows for the creation of applications that integrate seamlessly with ServiceNow’s existing IT service management offerings. This makes it particularly beneficial for organizations looking to enhance their IT operations and service delivery.
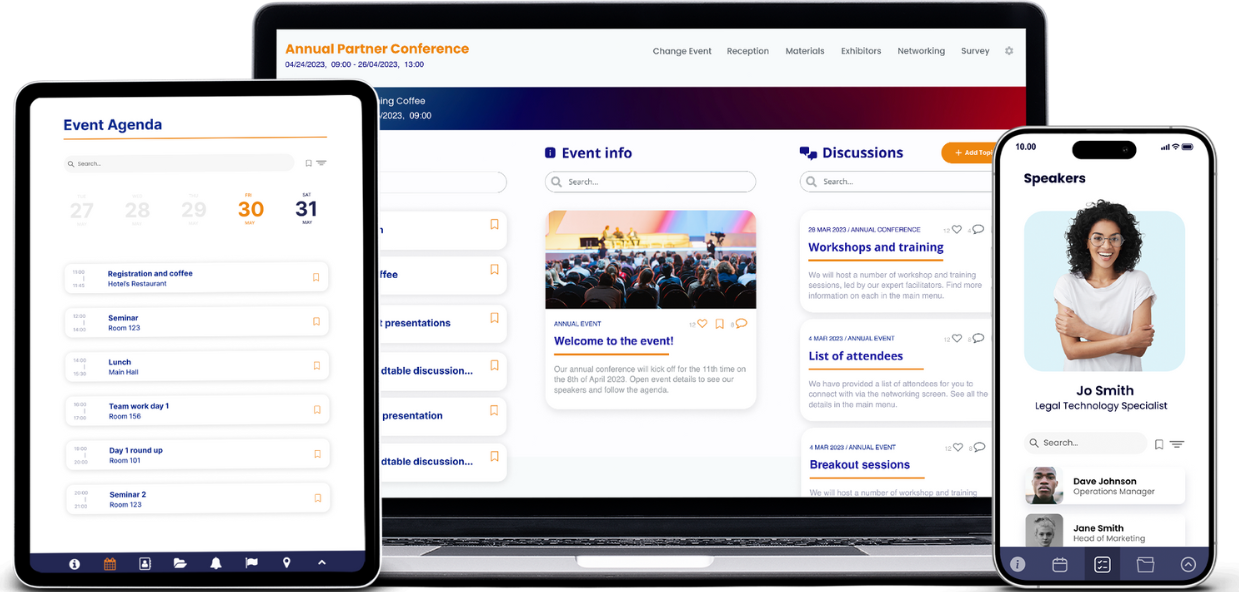
How Fliplet empowers you to become a citizen developer
Fliplet stands out as a powerful enabler for aspiring citizen developers, offering a suite of features and functionalities that simplify the app development process. Here’s how Fliplet can empower you in your citizen developer journey:
User-friendly interface
Fliplet’s intuitive drag-and-drop interface makes app development accessible, even for those with minimal technical expertise. This user-friendly approach allows you to easily create and customize apps, significantly lowering the entry barrier to app development.
Range of solutions
The platform offers a diverse selection of templates, catering to various business needs. These templates serve as a starting point, reducing the time and effort needed to build an app from scratch.
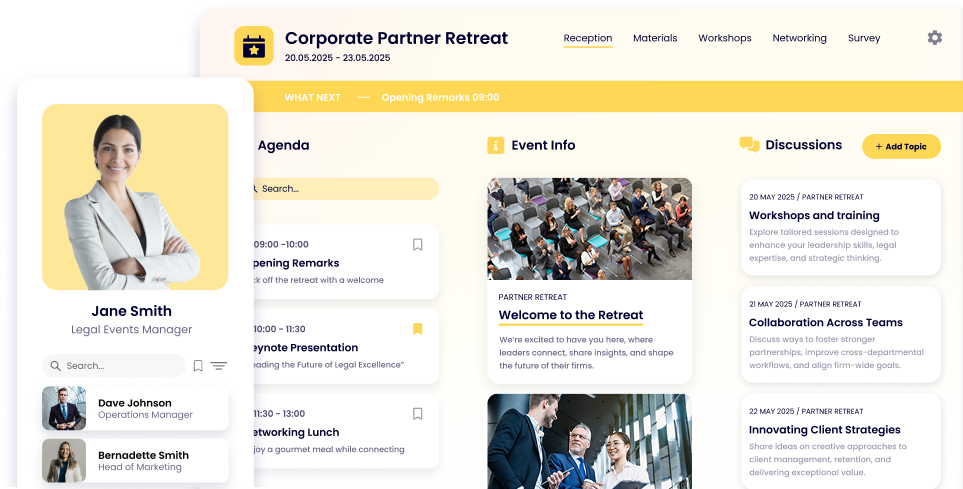
Events
Create an event app that can adapt to your event size and type. Whether you’re running a large hybrid conference or a small in-person roundtable, our solution will fit your event needs. Find out more.
Learning
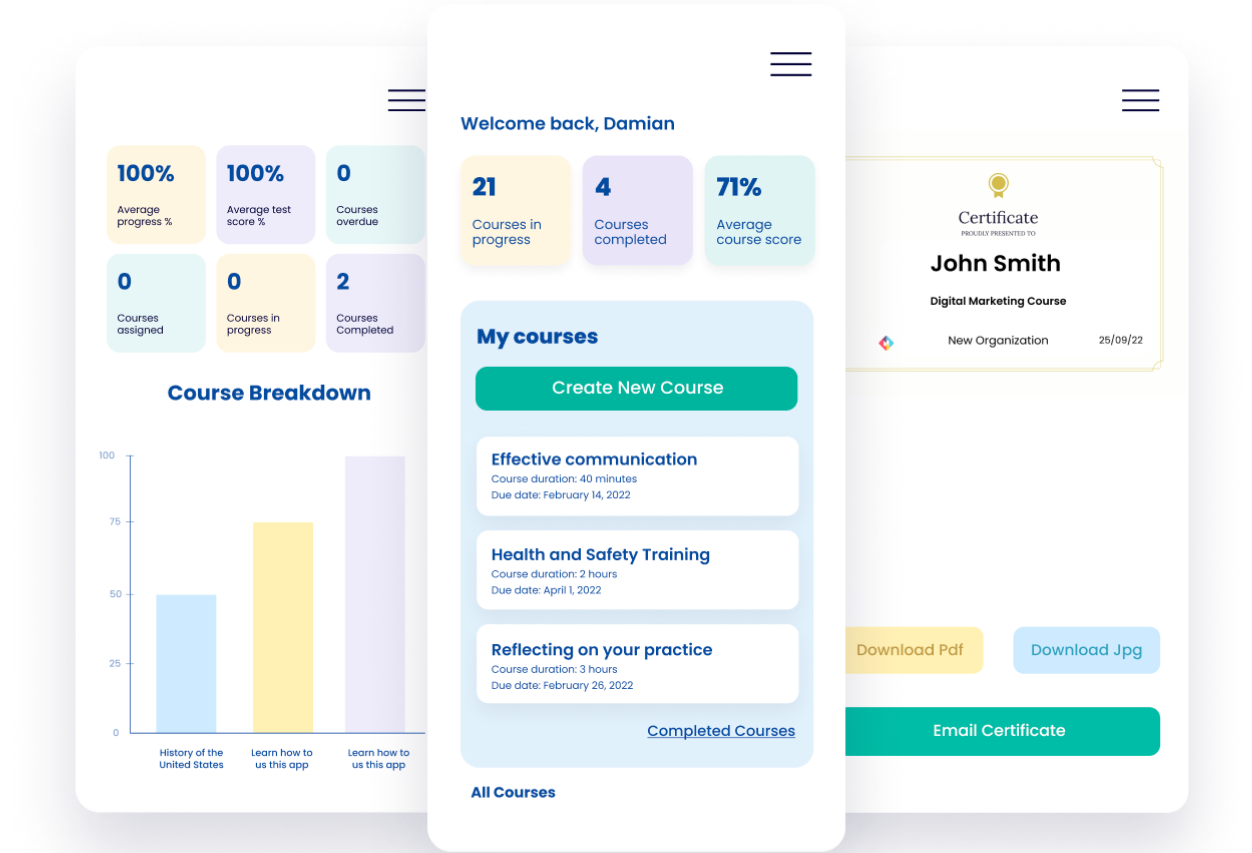
Build a learning solution that is interactive and accessible anywhere, anytime. From online courses to assessments, you will have the tools you need for effective learning experiences. Find out more.
Community
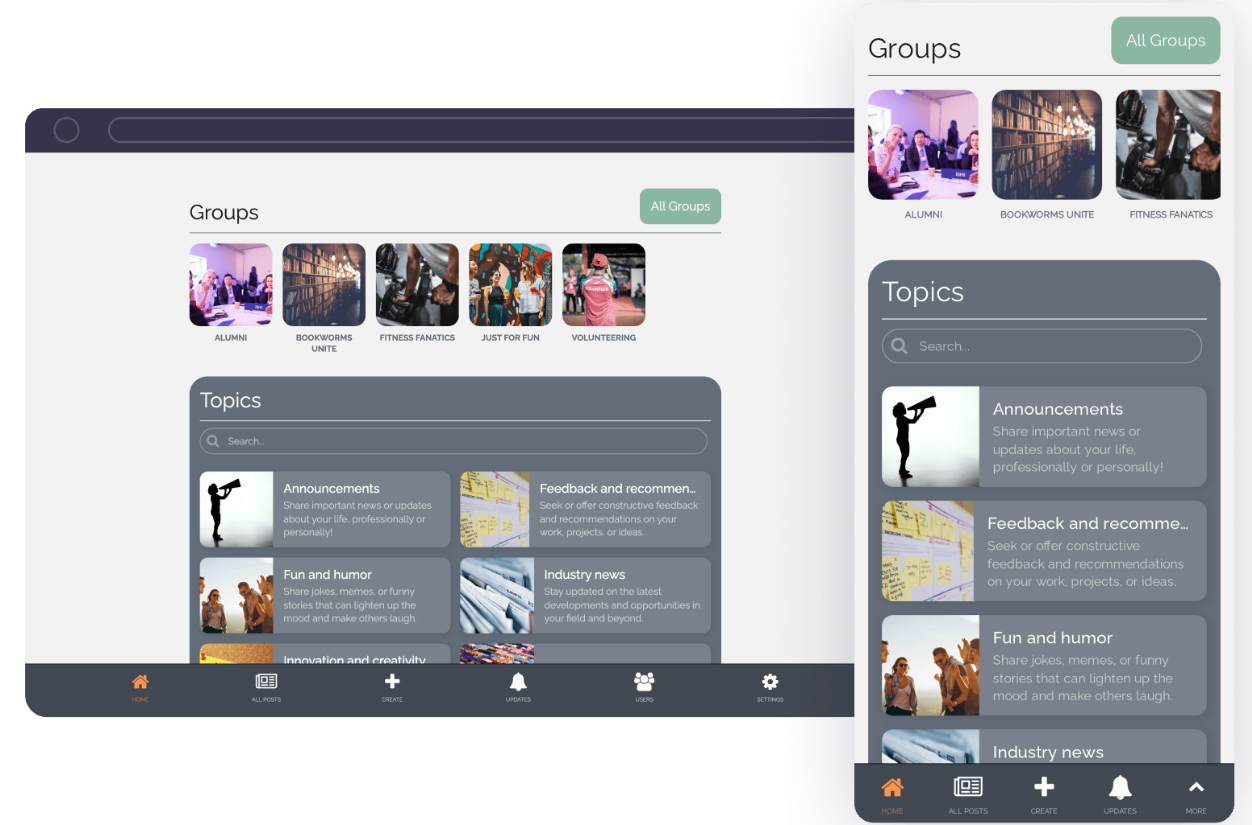
Engage your audience, form connections, and provide a centralized hub for community members to interact, share ideas, and stay informed. Find out more.
Directory
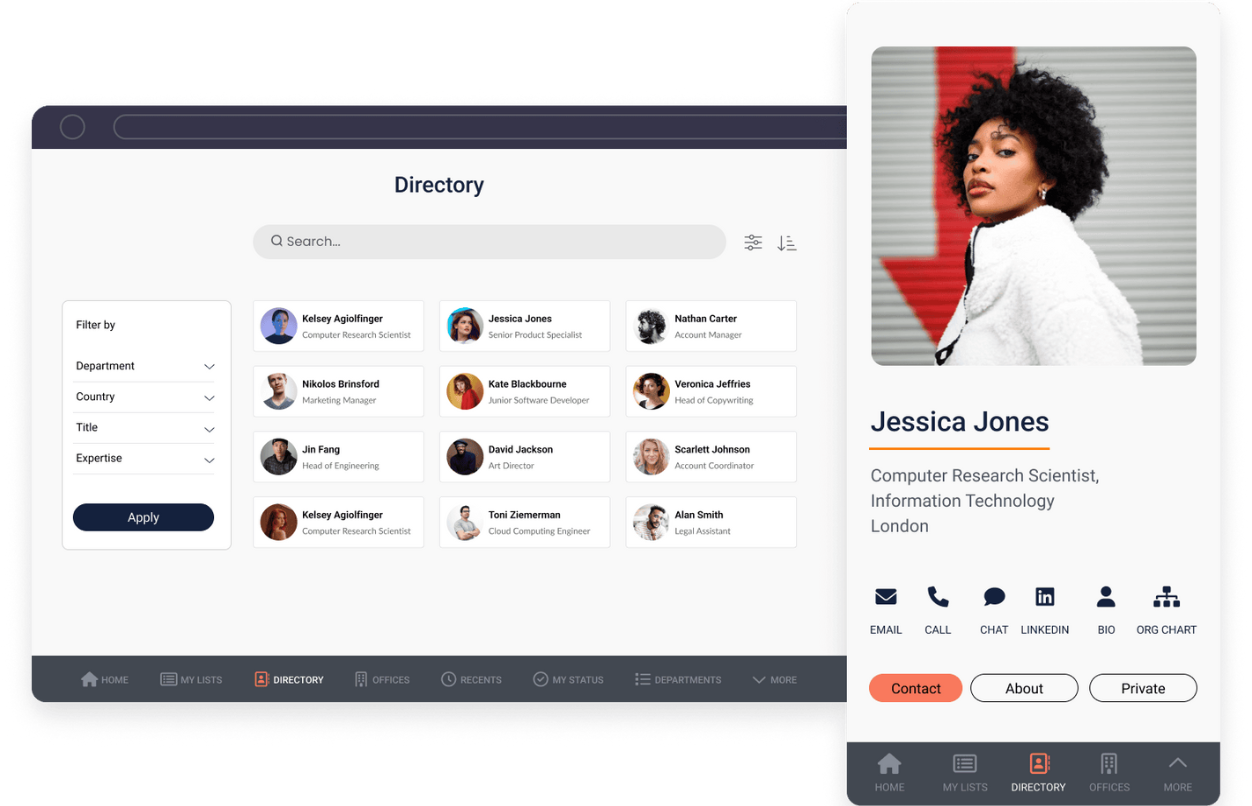
Facilitate team collaboration, and enhance accessibility and productivity. Clients, too, can use this solution to get in touch with the right personnel swiftly. Find out more.
Cross-platform publishing
One of Fliplet’s standout features is its ability to publish apps across multiple platforms, including Apple App Store, Google Play, and as web apps. This flexibility ensures that the applications you develop are widely accessible, regardless of the users’ preferred platform
No-code and low-code options
Catering to both non-technical users and those with some coding experience, Fliplet provides no-code and low-code options. This dual approach allows you to start with simple, no-code development and gradually progress to more customized solutions using low-code features.
Take a look at 8 ways to drive innovation at your organization with low-code/ no-code apps
Integration capabilities
Fliplet facilitates integration with existing systems and data, allowing you to create apps that seamlessly fit into your organization’s tech ecosystem.
Community and support
Fliplet provides access to a community of users and a wealth of support resources. This means you’re not just getting a tool but a supportive environment to learn, share, and grow as a citizen developer.
Hear from a Fliplet client and discover how Fliplet Empowered Citizen Developers at Gowling WLG.
By leveraging Fliplet, you can rapidly transform your innovative ideas into real-world applications. The platform empowers you to address specific business challenges, enhance productivity, and contribute to your organization’s digital transformation efforts. You can get started with Fliplet for free.
How can you find a job as a citizen developer?
Finding a job as a citizen developer is an exciting prospect, especially in a market where the demand for such roles is growing.
To start, build a portfolio showcasing your projects; this can be a strong negotiation tool for a better salary. In your resume, highlight your citizen development skills and experience, emphasizing how these have added value in terms of cost-saving or efficiency improvements, which are also key factors in salary discussions.
Networking is crucial, use platforms like LinkedIn to connect with industry professionals and share your work, attracting potential employers.
When searching for jobs, use keywords like ‘citizen developer’ or ‘low-code/no-code developer’ to find relevant listings, paying attention to the salary ranges to understand market rates.
Continuous learning and certification in relevant platforms can further boost your value. Your ability to translate business needs into digital solutions is highly valued by employers seeking to bridge the gap between technology and business.
Future trends in citizen development
Here are some key trends that are expected to shape the future of citizen development:
- Increased adoption of low-code/no-code platforms: With businesses seeking faster and more efficient ways to develop applications, the use of low-code and no-code platforms is expected to rise dramatically. These platforms will become more sophisticated, offering greater flexibility and more powerful features.
- Greater integration with AI: Artificial intelligence will increasingly be integrated into citizen development tools. This integration will enable more intelligent and automated app development processes, making it easier for citizen developers to create complex, data-driven applications. Take a look at our blog on How AI Will Disrupt App Development.
- Expansion into more business areas: Citizen development will expand beyond IT and into other business areas such as marketing, finance, and human resources. This will lead to more tailored and department-specific applications.
- Enhanced collaboration between IT and business units: As citizen development grows, there will be a stronger collaboration between IT departments and business units. This partnership will ensure that apps are not only quickly developed but also secure, compliant, and aligned with overall business strategies.
- Focus on mobile-first development: With the increasing use of mobile devices in the workplace, there will be a greater focus on mobile-first development in citizen development platforms, enabling the creation of more mobile-friendly apps. Take a look at The 10 Best Mobile Application Development Platforms 2023.
- Rise in citizen developer communities and training programs: As the field grows, so will the communities around it. We can expect to see more training programs and community support for citizen developers, enhancing knowledge sharing and skill development.
These trends indicate that citizen development is becoming an integral part of the digital transformation strategy for many organizations, empowering employees to contribute directly to the technological advancement and efficiency of their companies.
Conclusion: Citizen developer power comes with great responsibility
With the power to create and modify applications, citizen developers are equipped to drive innovation and efficiency within their organizations. However, with this power comes great responsibility.
Citizen developers must navigate the balance between speed and quality, ensuring that the applications they develop are not only effective but also secure and compliant with organizational and regulatory standards.
Also, as the field of citizen development continues to grow and evolve, platforms like Fliplet play a pivotal role. Fliplet empowers citizen developers with user-friendly tools for creating professional-grade applications, bridging the gap between technical expertise and business needs. The no-code/low-code platform creates a culture of innovation, enabling employees to contribute effectively to their organization’s digital transformation while maintaining high standards of quality and compliance.
As we move forward, the impact of citizen developers will only become more pronounced, making it an exciting time to be part of this transformative field.
FAQs
Who is a citizen developer?
A citizen developer is typically an employee within a business who, despite not having formal training in coding or software development, takes on the role of developing applications. They use low-code/no-code platforms to create or modify software that addresses specific business needs or improves processes. Citizen developers are often characterized by their deep understanding of their business domain, problem-solving skills, and ability to bridge the gap between technical capabilities and business requirements.
What is a citizen developer?
A citizen developer is an employee who creates or modifies business applications using low-code/no-code platforms, without needing formal expertise in software development. They typically work outside of IT departments but within the guidelines set by them. Their role is to bridge the gap between technical possibilities and business needs, leveraging their understanding of the business processes to develop practical, functional applications.
How to become a citizen developer?
Measuring the success of mobile app promotion can be done using various metrics, depending on your goals. Common metrics include the number of downloads, user retention rate, user reviews and ratings, and in-app engagement. Tools like Google Analytics for Mobile and platforms like App Annie or Sensor Tower can provide insights into these metrics. Additionally, the Return on Advertising Spend (ROAS) can help assess the effectiveness of paid promotional campaigns.
Is the salary of the citizen developer higher than the average salary?
The salary of a citizen developer can vary based on several factors including industry, location, level of expertise, and the specific tools they are skilled in. Generally, citizen developers with a strong understanding of business processes and the ability to create impactful applications can command competitive salaries. In many cases, their salary may be higher than the average, especially as they bring a unique blend of business insight and technical skill to their roles, which is increasingly valued in the digital transformation era. However, it’s important to note that salary comparisons should consider the specific context and job market conditions.